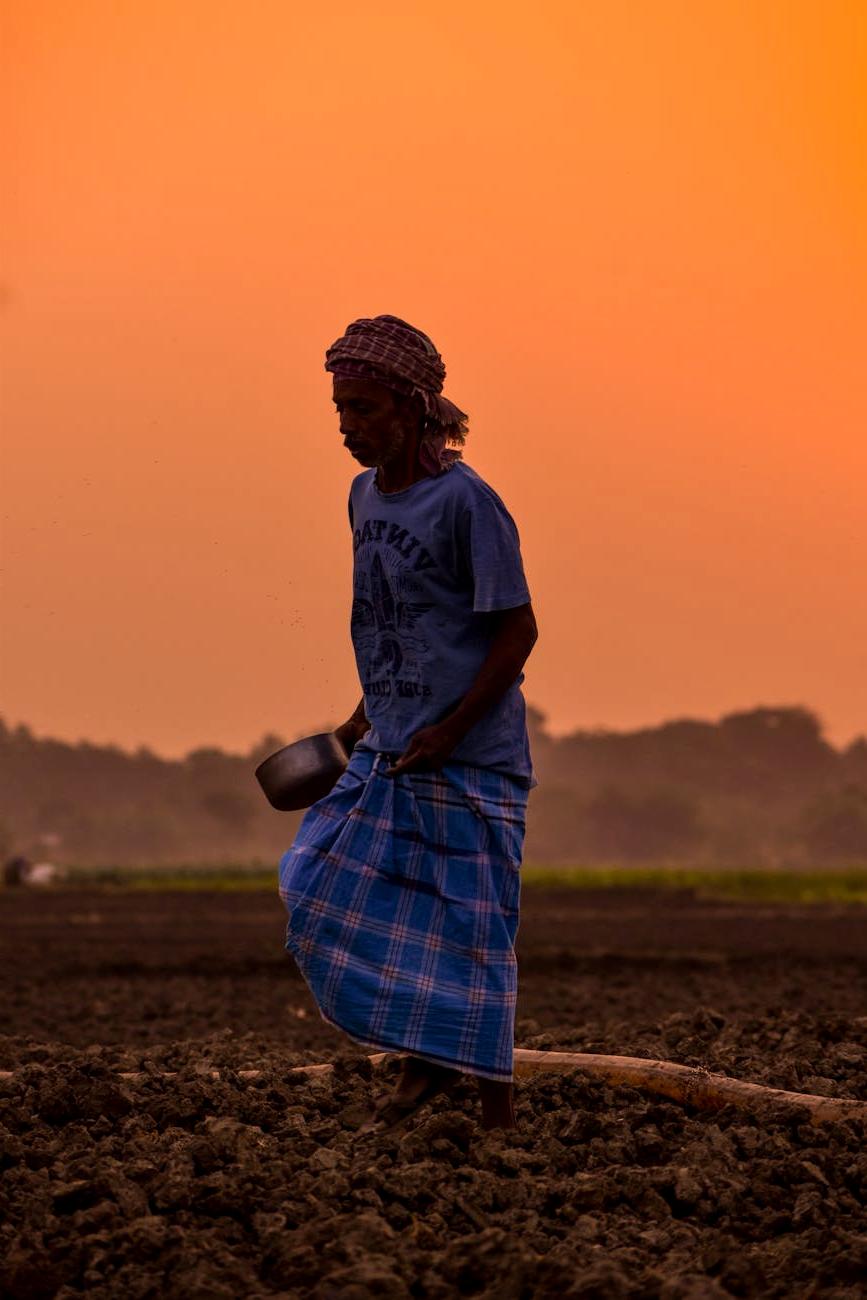

Protecting Our Planet From Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is one of the most significant environmental challenges facing our planet today. Learn about its causes, effects, and how we can work together to prevent it.
Learn More
Soil erosion is one of the most significant environmental challenges facing our planet today. Learn about its causes, effects, and how we can work together to prevent it.
Learn MoreSoil erosion is the displacement of the upper layer of soil, primarily by water, wind, or human activities.
This natural process becomes problematic when it accelerates due to human activities, leading to decreased soil fertility, reduced crop production, and damage to ecosystems and infrastructure.
Each year, approximately 24 billion tons of fertile soil are lost due to erosion. This is not just an environmental issue but an economic and social challenge that affects food security and community well-being worldwide.
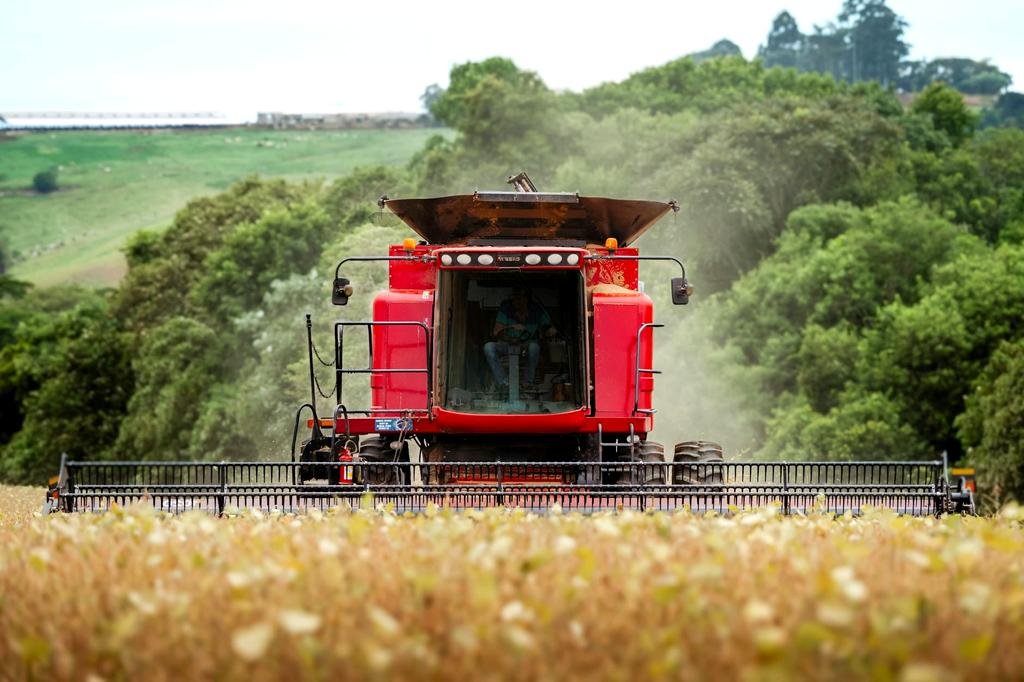

Understanding the primary factors that contribute to soil erosion is essential for developing effective prevention strategies.
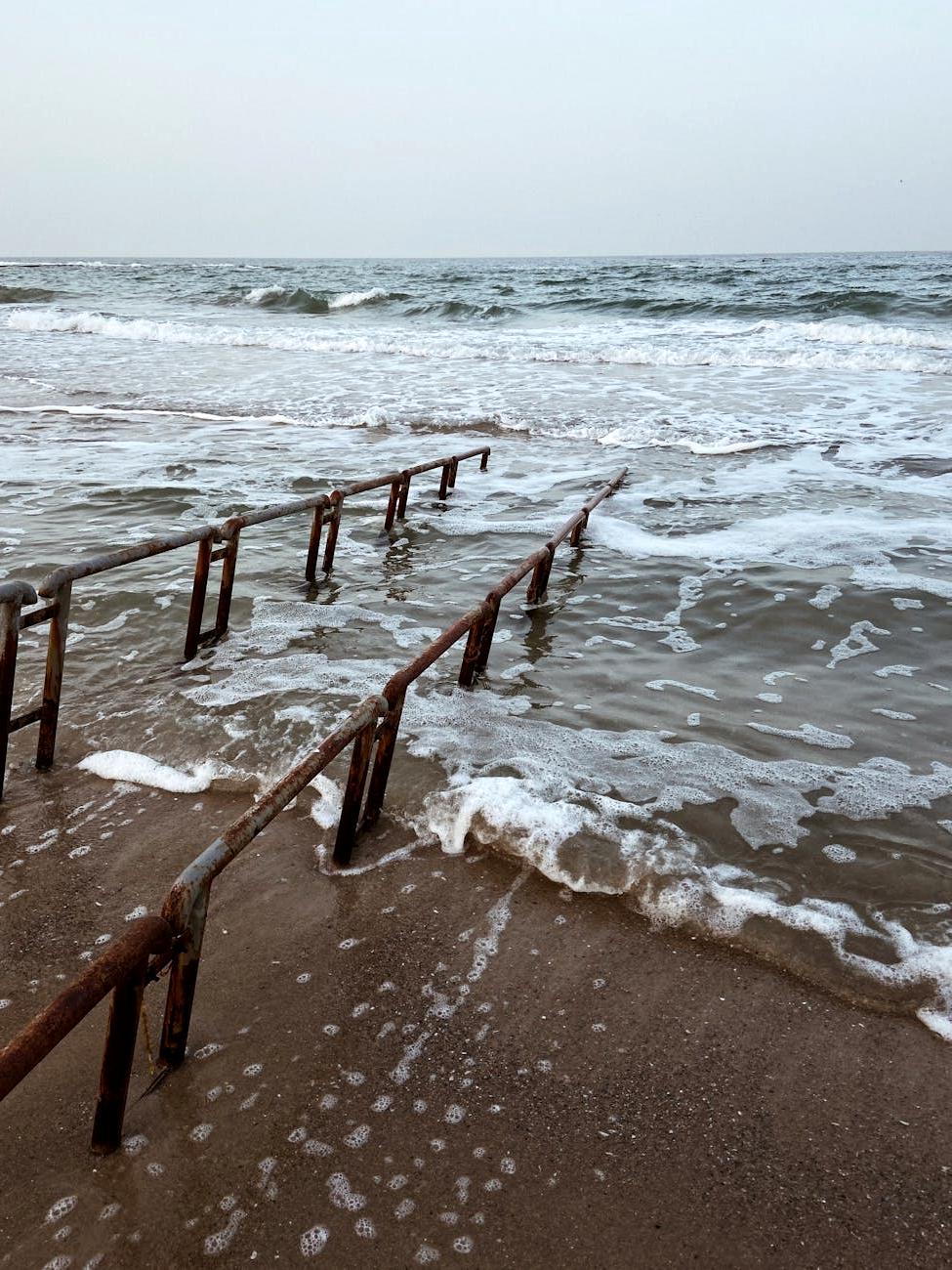

Rainfall and irrigation can wash away soil particles, especially on slopes and bare lands. This is the most common form of soil erosion worldwide.
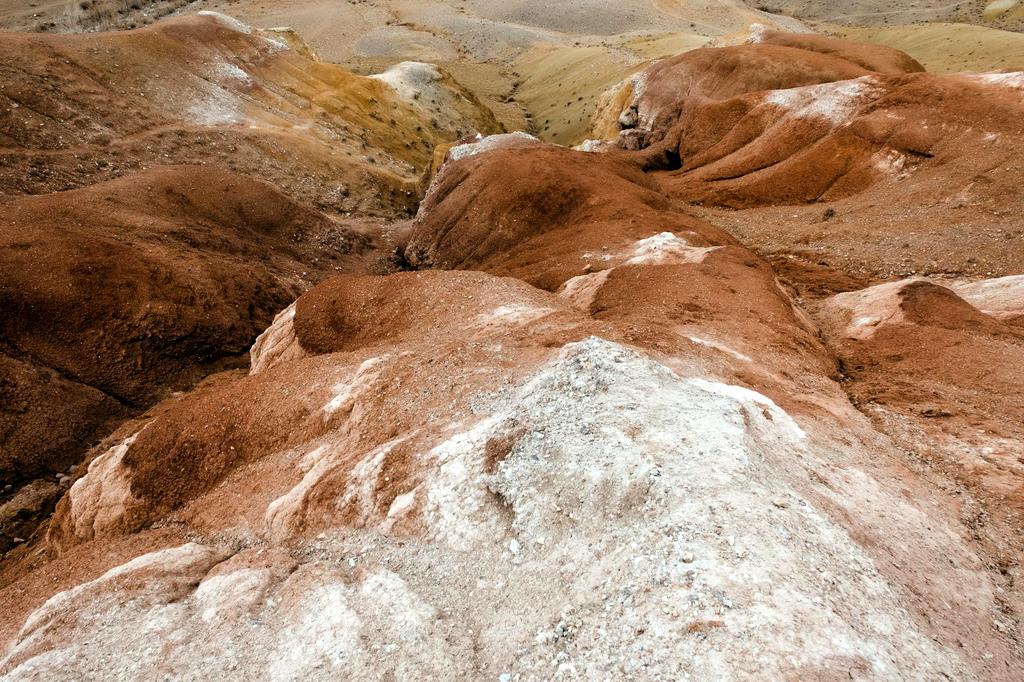

Strong winds can lift and transport soil particles over vast distances, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions with little vegetation cover.

Removing trees and vegetation eliminates the root systems that hold soil in place, making the land more susceptible to erosion.

Over-cultivation, improper tillage, and mono-cropping can degrade soil structure and make it more vulnerable to erosion forces.

Excessive livestock grazing removes protective vegetation cover and compacts soil, increasing runoff and erosion potential.

Urban development and construction projects often disturb large areas of soil, making them highly susceptible to erosion.
Tons of soil lost annually
Of global farmland degraded
Faster than natural formation
Tons of topsoil lost since 1950
Implementing these proven strategies can significantly reduce soil erosion and preserve this valuable natural resource for future generations.
Plowing and planting across slopes rather than up and down creates natural barriers that slow water runoff and prevent soil movement.
Planting crops like clover or rye during off-seasons keeps soil covered, adds organic matter, and improves soil structure.
Creating level platforms on slopes reduces runoff velocity and allows water to infiltrate the soil rather than washing it away.
Planting trees and shrubs as barriers reduces wind speed and helps prevent wind erosion in susceptible areas.
Maintaining vegetation along waterways creates natural filters that trap sediment and prevent stream bank erosion.
Reducing or eliminating plowing helps maintain soil structure, organic matter, and crop residue that protects against erosion.
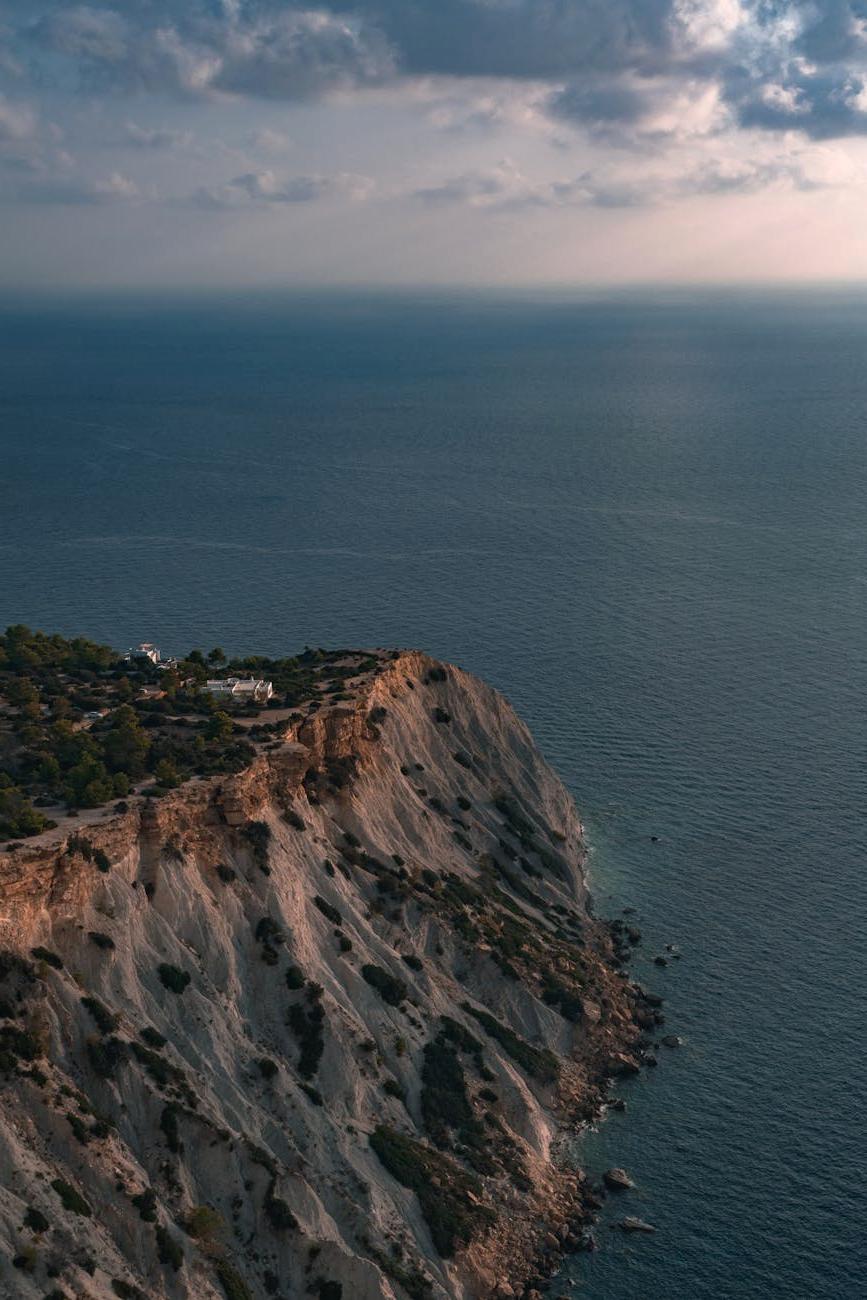
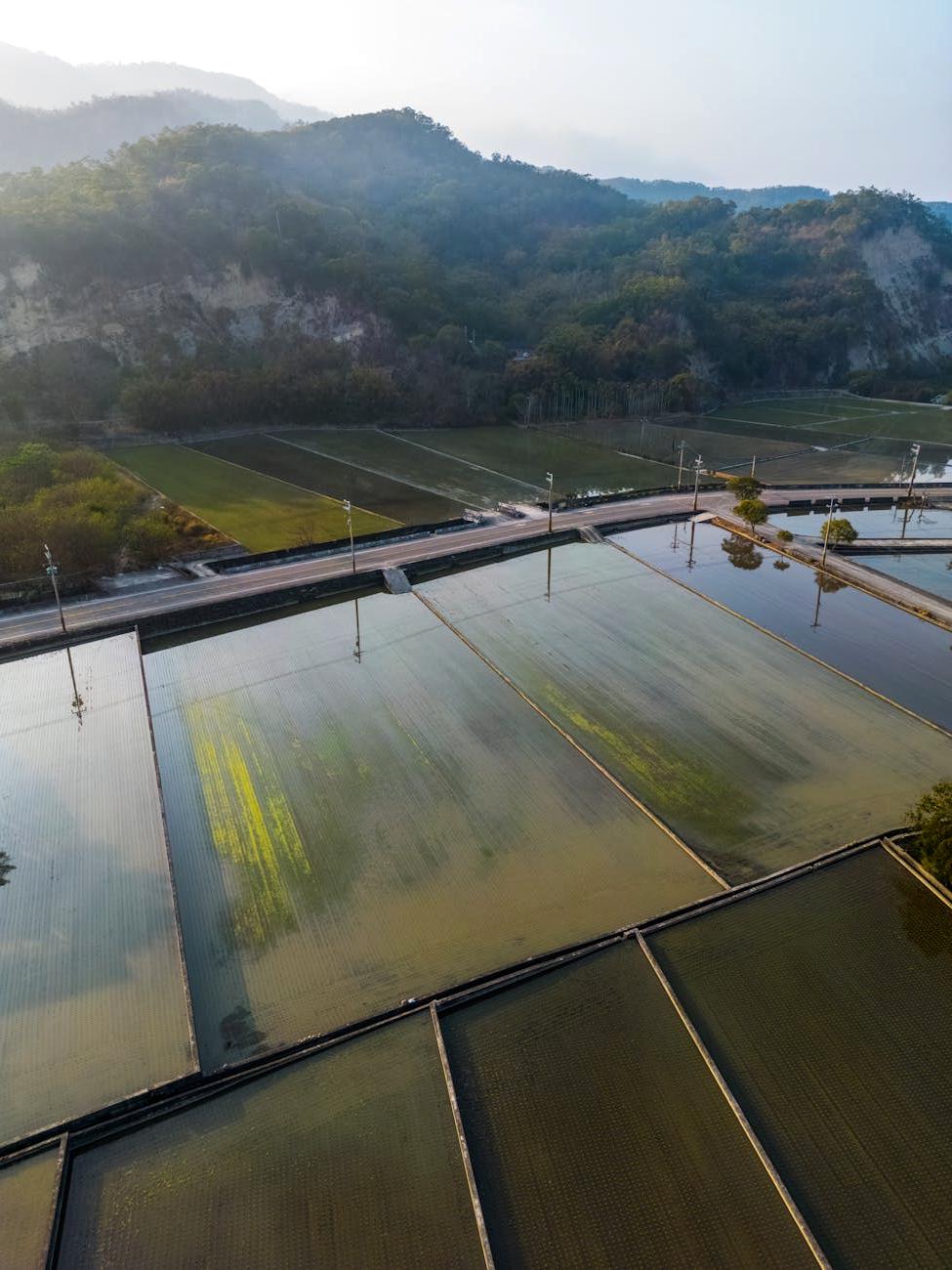
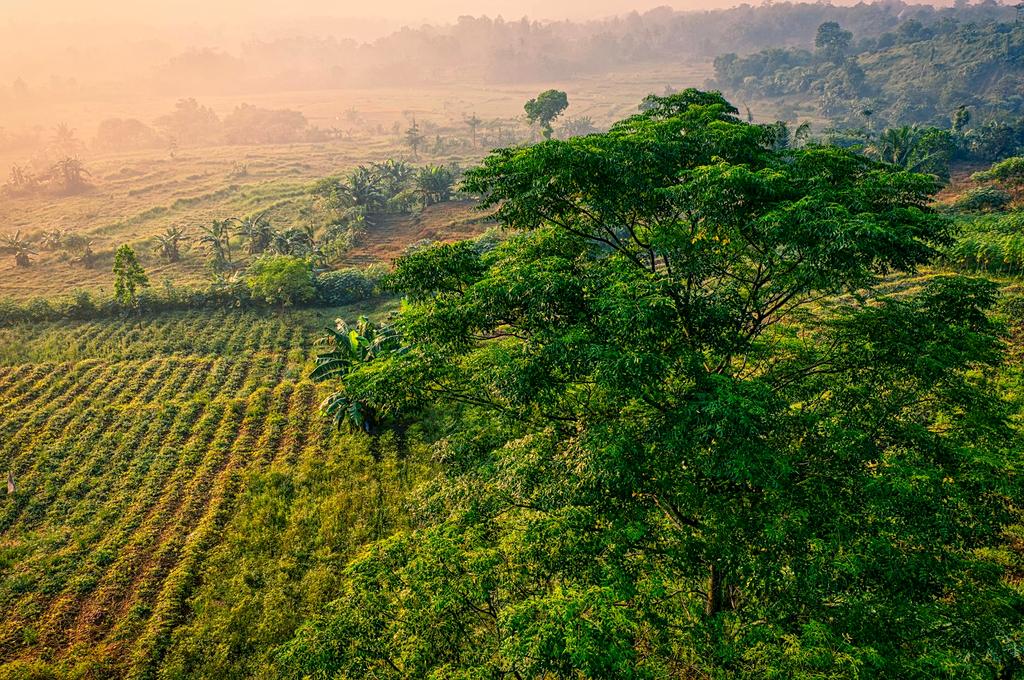
Visual evidence of erosion impacts and successful prevention measures around the world.





Subscribe to our newsletter to receive the latest information, research findings, and action plans to combat soil erosion in your community.